国际行业资讯 | 开启颜色可调纳米设备的新时代——有史以来最小的可切换颜色光源
作者:本站编辑
2023-08-24 09:56:18
53
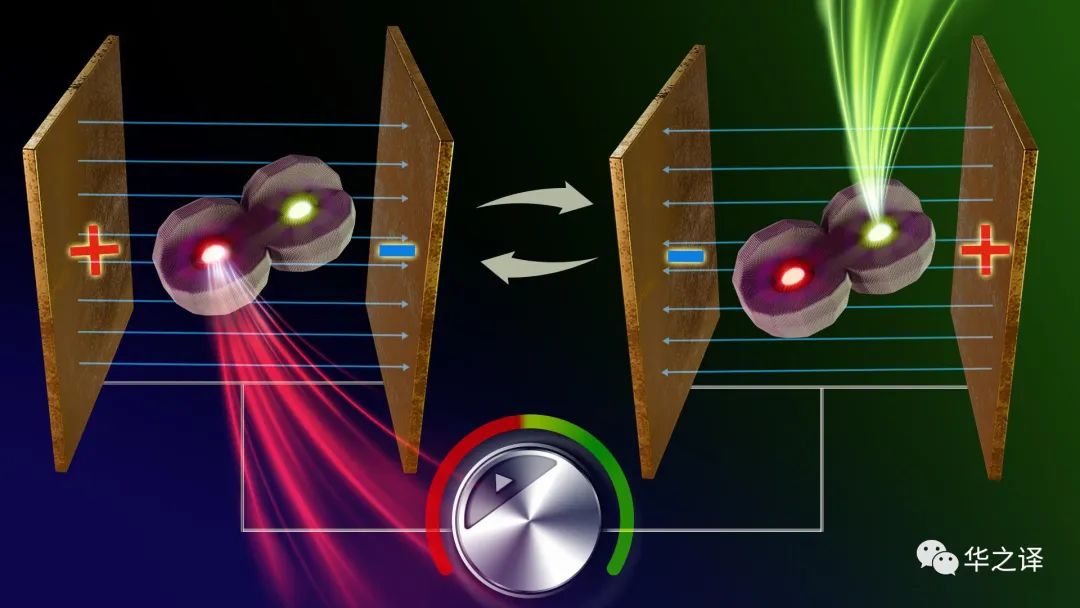
Nanocrystals, despite their ability to be color-tuned and their utility in diverse technologies, have been restricted in their usage due to the need for distinct nanocrystals for each color and dynamic switching between colors has not been possible.尽管纳米晶体能够进行颜色调节并且在多种技术中都有实用性,但由于每种颜色需要不同的纳米晶体,并且颜色之间的动态切换是不可能的,因此其使用受到限制。A team of Researchers at the Institute of Chemistry and The Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, including graduate student Yonatan Ossia with seven other members, and led by Prof. Uri Banin, have now come up with an innovative solution to this problem.耶路撒冷希伯来大学化学研究所和纳米科学与纳米技术中心的一个研究小组,包括研究生 Yonatan Ossia 和其他七名成员,在 Uri Banin 教授的领导下,现在提出了一种创新的解决方案 这个问题。By developing a system of an “artificial molecule” made of two coupled semiconductor nanocrystals that emit light in two different colors, fast and instantaneous color switching was demonstrated.通过开发由两个耦合的半导体纳米晶体组成的“人造分子”系统,该系统可以发出两种不同颜色的光,从而证明了快速、瞬时的颜色切换。Colored light and its tunability, are the basis to many essential modern-day technologies: from lighting, displays, fast optical fiber-communication networks, and more. Upon taking color-emitting semiconductors to the nanoscale (nano – one billionth of a meter, one hundred thousand times smaller than a human hair), an effect called quantum confinement comes into play: changing the size of the nanocrystal modifies the color of the emitted light. Thus, bright light sources can be obtained covering the entire visible spectrum.彩色光及其可调性是许多现代重要技术的基础:照明、显示、快速光纤通信网络等等。 将彩色发射半导体提升到纳米尺度(纳米——十亿分之一米,比人的头发小十万倍)时,一种称为量子限制的效应开始发挥作用:改变纳米晶体的尺寸会改变发射的颜色 光。 因此,可以获得覆盖整个可见光谱的明亮光源。Due to the unique color tunability of such nanocrystals, and their facile fabrication and manipulation using wet-chemistry, they are already widely used in high-quality commercial displays, giving them excellent color quality along with significant energy-saving characteristics. However, to this day, achieving different colors (such as needed for the different RGB pixels) required the use of different nanocrystals for each specific color, and dynamical switching between the different colors was not possible.由于此类纳米晶体独特的颜色可调性,以及使用湿化学法的简便制造和操作,它们已经广泛应用于高质量的商业显示器,赋予它们出色的色彩质量和显着的节能特性。 然而,直到今天,实现不同的颜色(例如不同 RGB 像素所需的颜色)需要针对每种特定颜色使用不同的纳米晶体,并且不同颜色之间的动态切换是不可能的。Although color tuning of single colloidal nanocrystals which behave as “Artificial atoms” has been previously investigated and implemented in prototype optoelectronic devices, changing colors actively has been challenging due to the diminished brightness inherently accompanying the effect, which only yielded a slight shift of the color.尽管之前已经在原型光电器件中研究并实现了充当“人造原子”的单个胶体纳米晶体的颜色调节,但主动改变颜色一直具有挑战性,因为伴随效果的固有亮度减弱,仅产生轻微的颜色变化 。The research team overcame this limitation, by creating a novel molecule with two emission centers, where an electric field can tune the relative emission from each center, changing the color, yet, without losing brightness. The artificial molecule can be made such that one of its constituent nanocrystals is tuned to emit “green” light, while the other “red” light.研究小组克服了这一限制,通过创建一种具有两个发射中心的新型分子,其中电场可以调整每个中心的相对发射,改变颜色,但不会损失亮度。 人造分子可以被制成使得其组成纳米晶体之一被调整为发出“绿”光,而另一个则发出“红”光。The emission of this new dual color emitting artificial molecule is sensitive to external voltage inducing an electric field: one polarity of the field induces emission of light from the “red” center, and switching the field to the other polarity, the color emission is switched instantaneously to “green”, and vice versa. This color-switching phenomenon is reversible and immediate, as it does not include any structural motion of the molecule. This allows one to obtain each of the two colors, or any combination of them, simply by applying the appropriate voltage on the device.这种新型双色发光人造分子的发射对引起电场的外部电压敏感:电场的一个极性引起“红色”中心的光发射,并将电场切换到另一极性,颜色发射被切换 立即变为“绿色”,反之亦然。 这种颜色转换现象是可逆且即时的,因为它不包括分子的任何结构运动。 这使得人们只需在设备上施加适当的电压即可获得两种颜色中的每一种或它们的任意组合。This ability to precisely control color tuning in optoelectronic devices while preserving intensity, unlocks new possibilities in various fields including in displays, lighting, and nanoscale optoelectronic devices with adjustable colors, and also as a tool for sensitive field sensing for biological applications and neuroscience to follow the brain activity. Moreover, it allows to actively tune emission colors in single photon sources which are important for future quantum communication technologies.这种在保持强度的同时精确控制光电器件颜色调节的能力,开启了各个领域的新可能性,包括显示器、照明和具有可调节颜色的纳米级光电器件,并且还可以作为生物应用和神经科学的敏感场传感工具 大脑活动。 此外,它还可以主动调整单光子源的发射颜色,这对于未来的量子通信技术非常重要。Prof. Uri Banin from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem explained, “Our research is a big leap forward in nanomaterials for optoelectronics. This is an important step in our exposition of the idea of “nanocrystal chemistry” launched just a few years ago in our research group, where the nanocrystals are building blocks of artificial molecules with exciting new functionalities. Being able to switch colors so quickly and efficiently on the nanoscale as we have achieved has enormous possibilities. It could revolutionize advanced displays and create color-switchable single photon sources.”耶路撒冷希伯来大学的 Uri Banin 教授解释说:“我们的研究是光电子纳米材料领域的一大飞跃。 这是我们研究小组几年前推出的“纳米晶体化学”理念的重要一步,其中纳米晶体是具有令人兴奋的新功能的人造分子的构建块。 能够像我们这样在纳米尺度上如此快速有效地切换颜色具有巨大的可能性。 它可以彻底改变先进的显示器并创建可切换颜色的单光子源。”By utilizing such quantum dot molecules with two emission centers, several specific colors of light using the same nanostructure can be generated. This breakthrough opens doors to developing sensitive technologies for detecting and measuring electric fields. It also enables new display designs where each pixel can be individually controlled to produce different colors, simplifying the standard RGB display design to a smaller basis of pixels, which has the potential to increase the resolution and energy savings of future commercial displays.通过利用这种具有两个发射中心的量子点分子,可以使用相同的纳米结构产生几种特定颜色的光。 这一突破为开发用于检测和测量电场的敏感技术打开了大门。 它还支持新的显示设计,其中每个像素都可以单独控制以产生不同的颜色,从而将标准 RGB 显示设计简化为更小的像素基础,这有可能提高未来商业显示器的分辨率和节能效果。This advancement in electric field-induced color switching has immense potential for transforming device customization and field sensing, paving the way for exciting future innovations.电场引起的颜色切换的这一进步对于改变设备定制和场感测具有巨大的潜力,为令人兴奋的未来创新铺平了道路。Reference: “Electric-field-induced colour switching in colloidal quantum dot molecules at room temperature” by Yonatan Ossia, Adar Levi, Yossef E. Panfil, Somnath Koley, Einav Scharf, Nadav Chefetz, Sergei Remennik, Atzmon Vakahi and Uri Banin, 3 August 2023, Nature Materials.参考文献:“室温下胶体量子点分子中电场诱导的颜色转换”,作者:Yonatan Ossia、Adar Levi、Yossef E. Panfil、Somnath Koley、Einav Scharf、Nadav Chefetz、Sergei Remennik、Atzmon Vakahi 和 Uri Banin,3 2023 年 8 月,《自然材料》。DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01606-0DOI:10.1038/s41563-023-01606-0The study was funded by the European Research Council.


